Petya/NotPetya Ransomware Detection for the Modern Enterprise

A new version of the Petya malware is spreading globally, including the European Union, Ukraine and Russia. It has already impacted many organizations, both large and small, and has compromised systems at Ukraine’s central bank, its state telecommunications company, municipal metro, and Kiev’s Boryspil International Airport.
Background
Petya ransomware is powered by Shadow Brokers exploits, which were leaked earlier this year. After compromising a system, the malware encrypts the data using a private key, and prevents users from accessing the system until it is restored or decrypted. The initial infection vector for this campaign appears to be a poisoned update for the MeDoc software suite, a tax software package used by many Ukrainian organizations. The malware then infects systems that are vulnerable to MS17-010 and spreads laterally across the infrastructure.
Note: The Petya malware creates a scheduled task which reboots up to one hour after infection. If the task is removed before execution, it does not reschedule, buying you some time.
Similar to the WannaCry ransomware that infected systems globally earlier this year, Petya takes advantage of known vulnerabilities that already have patches. In a world where malware threats arise every day, chasing daily threats is not advised. Organizations everywhere and of every size need a more strategic approach to proactively manage security threats (and protect themselves and their customers) by implementing good cyber hygiene practices, including regular patching, updates, backups, and continuous monitoring.
How Tenable can help
Patch vulnerabilities
Tenable customers should immediately patch systems vulnerable to MS17-010 if you haven’t already done so. Tenable.io™ Vulnerability Management has the following four plugins, released earlier this year, to detect vulnerable systems:
| Plugin ID | Plugin Title/Comments | Exploits |
|---|---|---|
|
97737 |
MS17-010: Security Update for Microsoft Windows SMB Server (4013389) |
ETERNALBLUE ETERNALCHAMPION ETERNALROMANCE ETERNALSYNERGY WannaCry EternalRocks |
|
97833 |
MS17-010: Security Update for Microsoft Windows SMB Server (4013389) uncredentialed check |
ETERNALBLUE ETERNALCHAMPION ETERNALROMANCE ETERNALSYNERGY WannaCry EternalRocks |
Malware scan
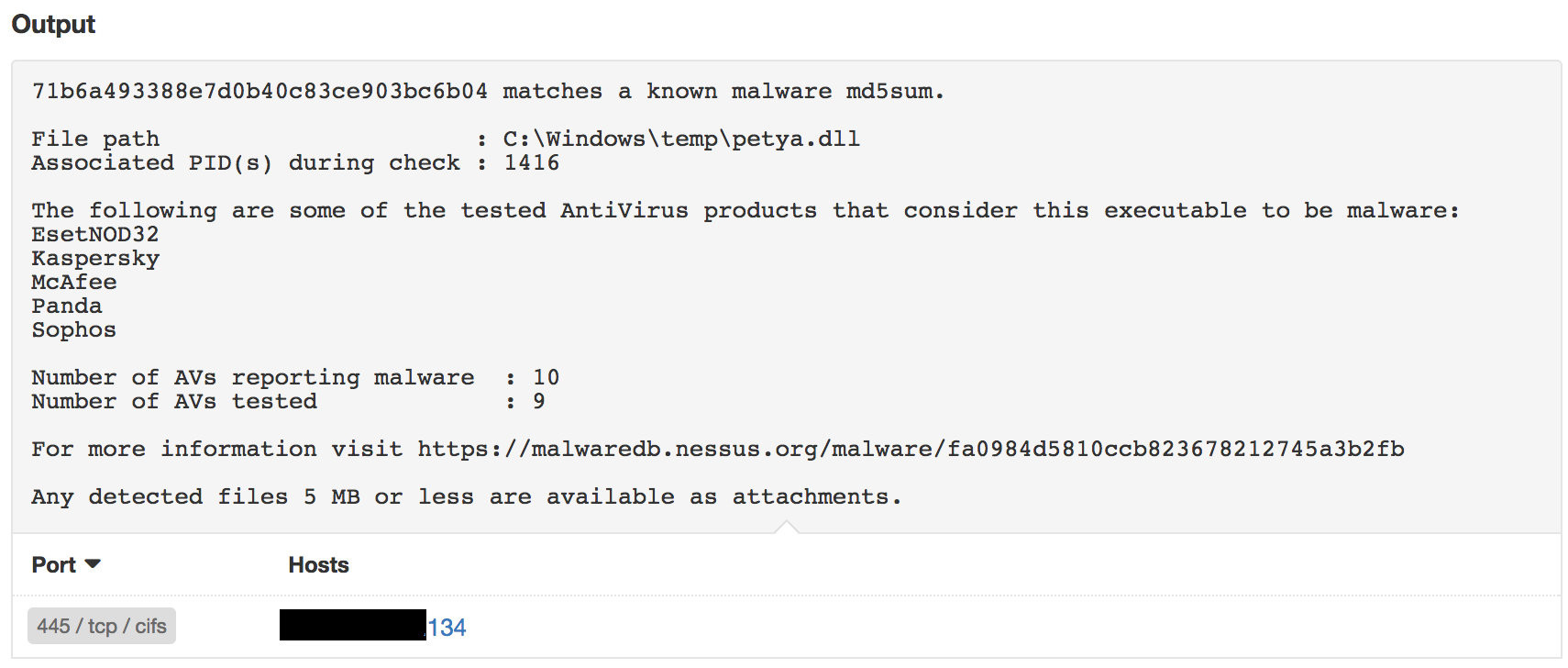
Tenable customers can use the Malware Scan Policy in Tenable.io™ or SecurityCenter™ to detect machines infected with Petya, and the results will be reported under plugin 59275:
YARA detection
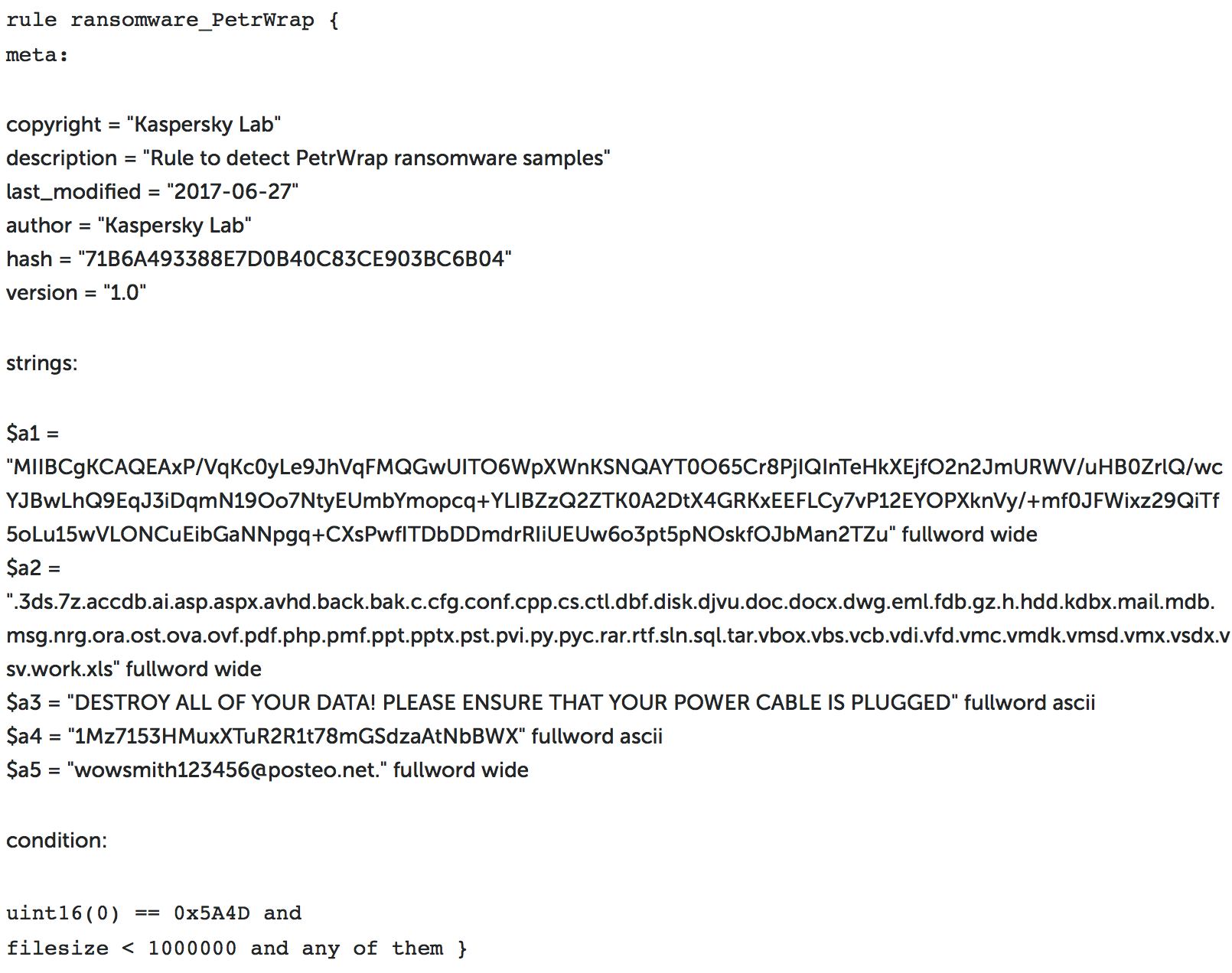
Tenable customers can also use YARA rules to identify infected systems through the Malicious File Detection Using YARA Nessus plugin.
Here’s a sample rule from Kaspersky which can be used with Nessus to detect the Petya malware :
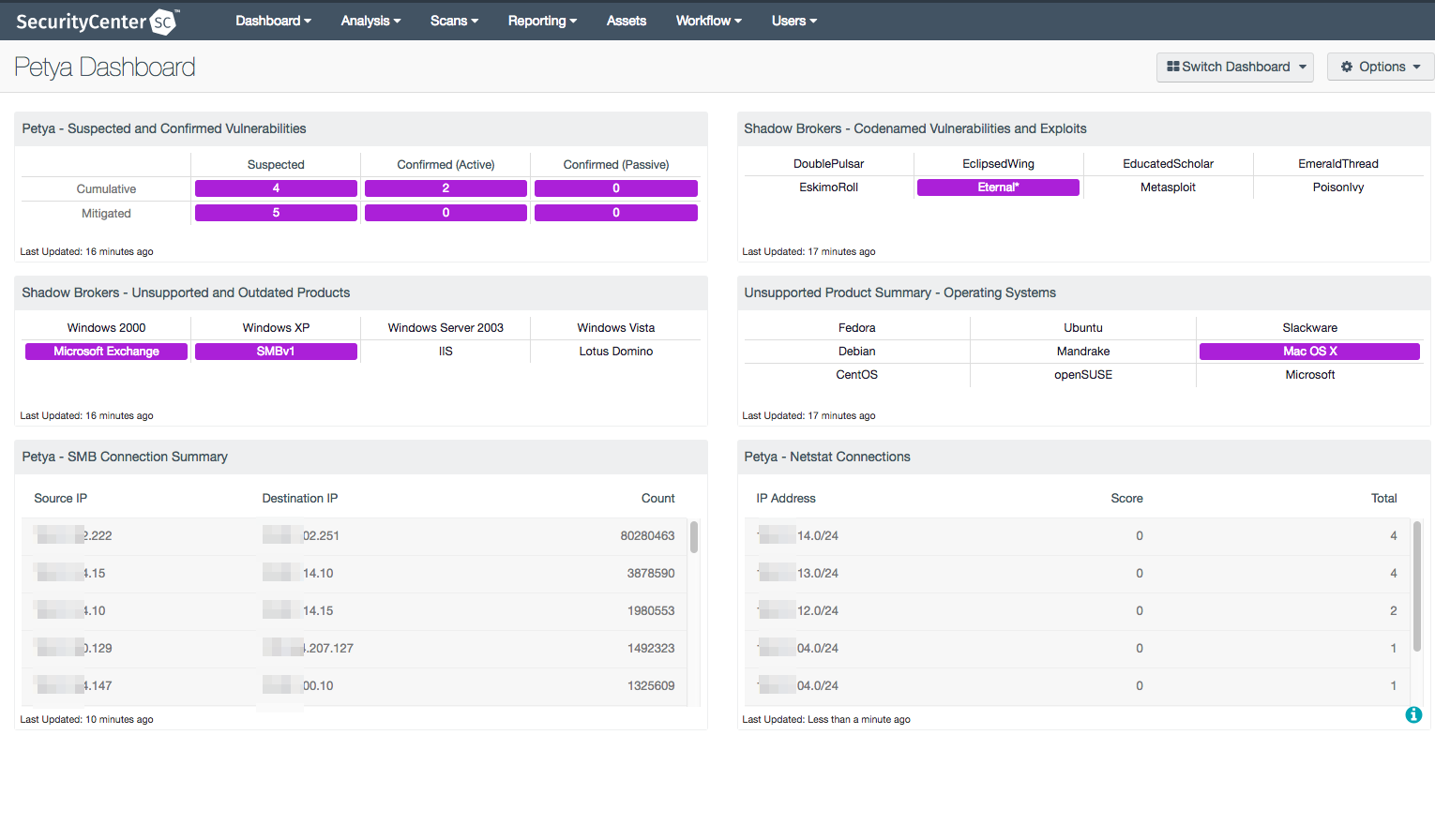
Dashboards
The Petya dashboard uses all the available methods mentioned above to consolidate the data for easy understanding of the systems most likely affected or at risk from the malware. The components bring in netstats from Nessus and the Nessus Network Monitor, and also display the content related to missing patches associated with SMB vulnerabilities.
Wrap-up
Most ransomware exploits well-known vulnerabilities that already have patches available. Implementing a proactive security program that includes regular patching and system updating is one of the best strategies you can use to prevent malware from infecting your systems. Make it a regular habit to patch and protect.
For more information
- Learn more about Tenable.io, the first vulnerability management platform for all modern assets
- Get a free 60-day trial of Tenable.io
Many thanks to the Tenable research team for their contributions to this blog.
Updated June 28, 2017. Initial research suggested that CVE-2017-0199 was a potential infection vector; we are doing additional research into that issue.
- Malware
- Plugins
- Vulnerability Scanning