by Cody Dumont
June 29, 2017
A new version of ransomware has been detected in the wild called Petya. Petya encrypts the hard drive making the system unusable. This dashboard uses all the available methods to consolidate the data for easy understanding of the systems most likely affected by or at risk to the malware.
Petya is powered by Shadow Brokers exploits, which were leaked earlier this year, and appears to be a straightforward ransomware program. Once the malware has infected a computer, the virus encrypts each computer with a private key, rendering the machine unusable until the system is decrypted. The ransomware leverages a couple of vulnerabilities to quickly spread across the organization. Petya first leverages CVE-2017-0199, a vulnerability in Microsoft Office documents that enables the execution of malicious HTA files. The malware then infects systems that are vulnerable to MS17-010 in order to spread laterally across the infrastructure.
Similar to other recent ransomware that infected systems globally earlier this year, Petya takes advantage of known vulnerabilities that already have patches.
Organizations who are reactive to new threats will always find themselves trying to catch up to malicious adversaries. Organizations everywhere and of every size need to implement a more holistic approach to identifying deficiencies in risk management. To implement a good cyber hygiene practice, the organization should start with a vulnerability management process using SecurityCenter Continuous View.
This dashboard uses several methods to detect vulnerability to the Petya cyberattack, including Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE), connection monitoring with Netstat, and malicious traffic detection using the Nessus Network Monitor. The collection of components brings a view of vulnerabilities related to Petya and other by Shadow Brokers exploits into one place to easily identify vulnerable systems.
This dashboard is available in the SecurityCenter Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the SecurityCenter Feed under the category Threat Detection & Vulnerability Assessments.
The dashboard requirements are:
- SecurityCenter 5.5.0
- Nessus 6.10.8
- Nessus Network Monitor 5.3.0
Tenable SecurityCenter is the market-defining continuous network monitoring solution, which assists organizations in securing their internal network. While SecurityCenter is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, there are several informational plugins and collected events that help analysts anticipate systems that could be at risk to new threats such as Petya. Active scanning periodically examines systems to determine vulnerabilities and compliance concerns. Agent scanning enables scanning and detection of vulnerabilities on transient and isolated devices. SecurityCenter Continuous View provides an organization with the most comprehensive view of risks within the network and the intelligence needed to support effective vulnerability remediation efforts.
This Dashboard contains the following components:
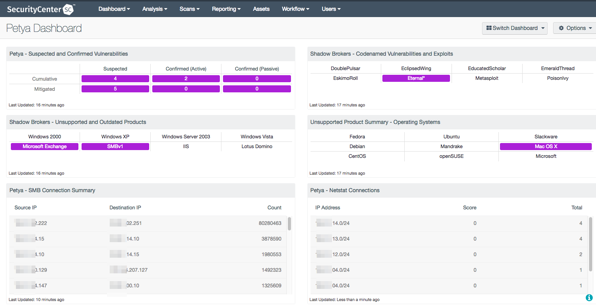
Petya - Suspected and Confirmed Vulnerabilities: This matrix provides the analysts with a view of the systems that are suspected or confirmed to be vulnerable to Petya infection.
Shadow Brokers - Unsupported and Outdated Products: This matrix specifically identifies the unsupported or outdated operating systems or services known to be particularly vulnerable to exploitation. Each cell filters for outdated or unsupported versions of a specific product and turns purple upon detection. Security teams can use this component to determine which systems require immediate updates in order to remediate the detected vulnerabilities.
Petya - SMB Connection Summary: This table shows a list of host-to-host communications that have had port 445 event logs generated, which indicates SMB-related traffic.
Shadow Brokers - Codenamed Vulnerabilities and Exploits: This matrix displays the codenamed vulnerabilities and associated exploits published by the Shadow Brokers hacking group. Each cell filters for a specific vulnerability or exploit and turns purple when at least one instance is detected. Security teams can use this component to quickly identify which vulnerabilities their network may be susceptible to.