Patch or Risk Being Breached: Tenable.io and the Verizon 2017 DBIR

According to the 2017 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), time to patch plays a critical role in the risk exposure to your network. The DBIR states (page 13) “research has shown that vulnerabilities are either patched during that initial cycle or tend to hang around for a long time,” meaning that if you don’t patch early and often, then patches don’t get applied and you are at risk of a breach or ransomware attack. Have you implemented the right mitigating controls or has your organization ignored the possible impact of not patching a system? Tenable.io™ can help you understand your current risk exposure by monitoring the time taken to patch vulnerabilities.
If you don’t patch early and often, you are at risk of a breach or ransomware attack
Attackers continue to be successful due to unpatched applications
When discussing risk mitigation strategies I often hear, “The patching process is just one part of our overall security strategy.” In some cases, organizations allow patching to take a backseat to focus on other efforts. The DBIR offers potential justifications (page 13) for organizations failing to patch, “that other controls are in place, or the vulnerabilities may not be exploitable.” Security operation teams may tend to focus more on managing devices that restrict access, including firewalls, intrusion prevention and detection systems. While keeping an unwanted visitor out of your environment is important, patching is critical. Breaches occur by giving an attacker the opportunity to compromise existing vulnerabilities, gaining a greater foothold within your organization.
Practicing good patch management is critical in maintaining a secure environment
Today’s environments are no longer defined by clear boundaries, and access to information is harder to control using traditional methods. Patching applications such as web browsers remains a critical effort. The DBIR (page 41) advises to “Prioritize patching vulnerabilities associated with browser exploitation. This includes the browser software, but also plug-ins.” Likewise, remote devices and/or mobile employees potentially increase risk to your network, as they can leave the protective confines of the network and should be patched appropriately.
Poor security results in organizational cost increases
Since 2008, the Verizon DBIR has provided organizations with insight into managing their risk and avoiding cybersecurity pitfalls. Over the years, we have seen a disturbing trend, where exploits enabled by vulnerabilities that have had patches for at least six months prior to the attacks have skyrocketed. This pattern can easily be broken by timely patch management programs.
For example, according to the DBIR (page 68), “In September, Yahoo announced a data breach from 2014 that compromised the accounts of 500 million.” The Yahoo data breach was made possible by exploiting an unpatched vulnerability in an Account Management Tool. The exploit eventually led to executive resignations and a loss of $350 million of revenue in a buyout offer. These types of attacks can also result in a tarnished reputation. All these consequences are the result of patch management not being practiced on a regular and timely basis.
Tenable.io solutions
Your organization’s patching process should focus on coverage and consistency. Patching efforts should also be aligned with other important parts of your cybersecurity program, such as firewalls, IDS and other defenses. Tenable.io offers several options to support your patch management program.
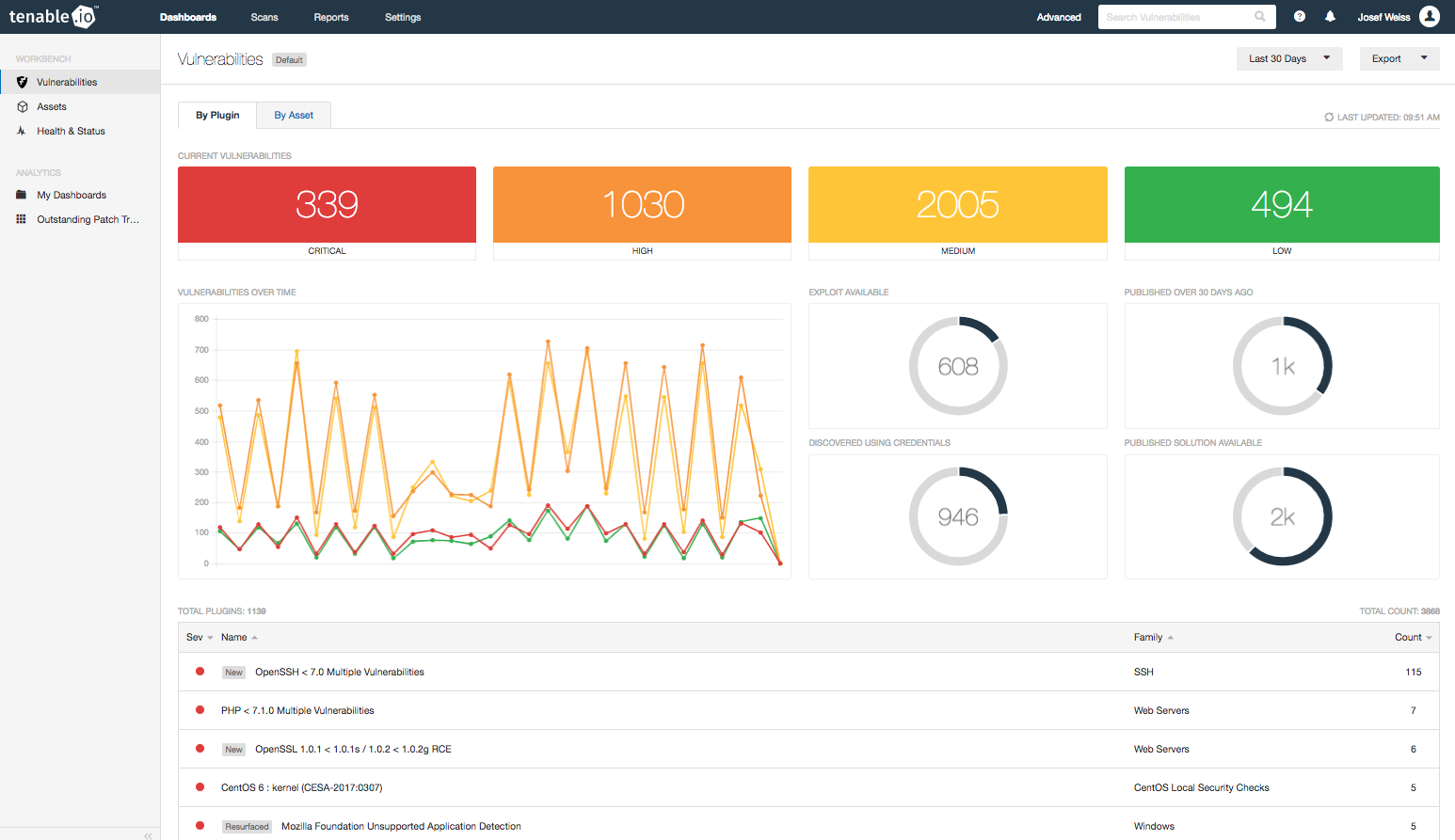
At the center of Tenable.io is the Vulnerability Workbench. You can view the cumulative vulnerability data here. You can also use the Advanced Search filters to quickly and easily display details of currently missing patches and other vulnerabilities.
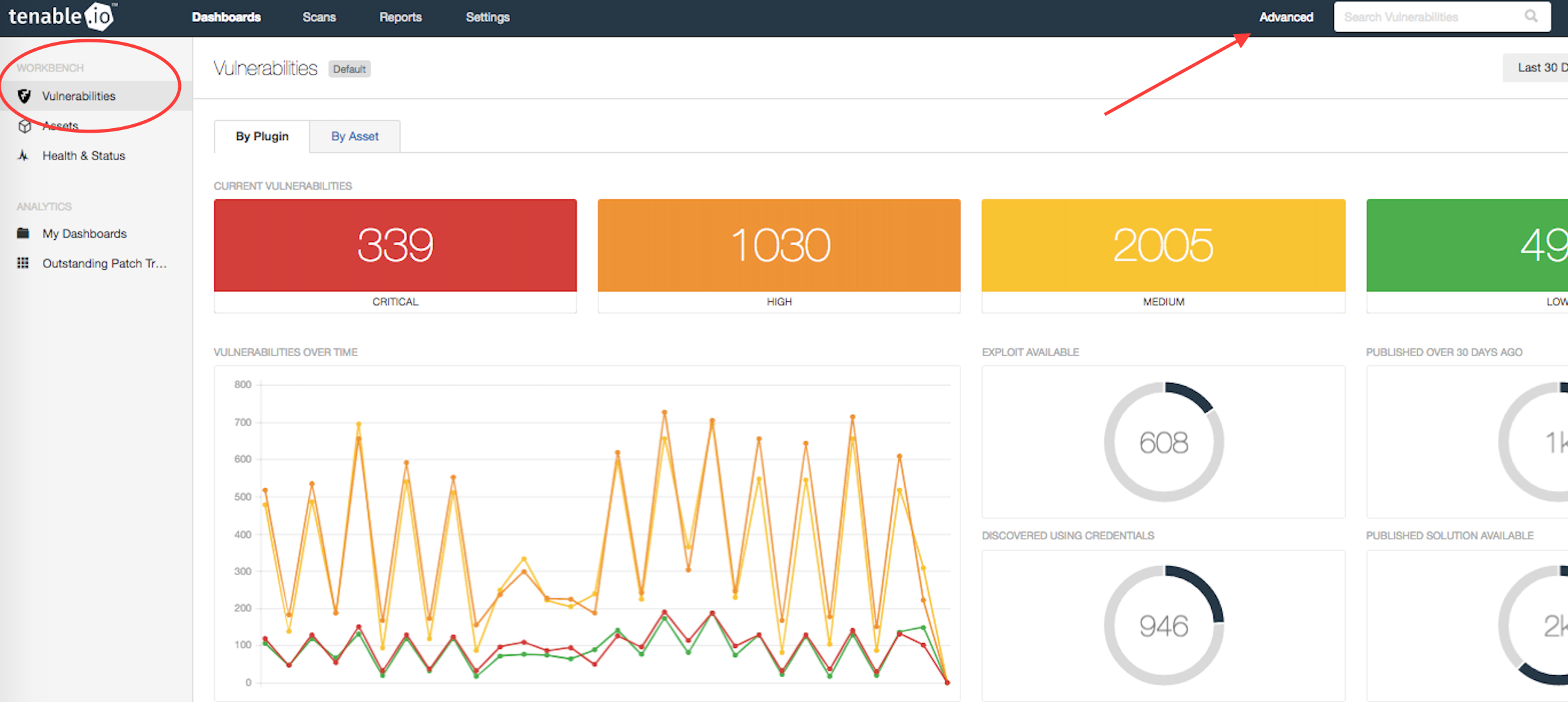
From the vulnerability workbench, select Advanced on the top navigation bar to access the Advanced Search window.
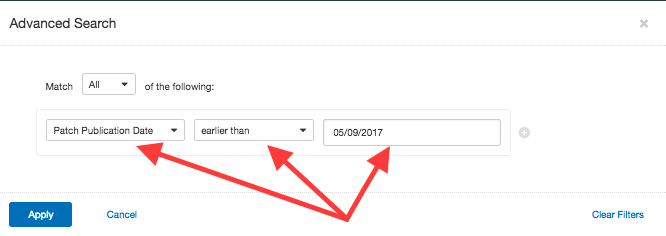
Set the filter to Patch Publication Date and select a time, such as earlier than today’s date.
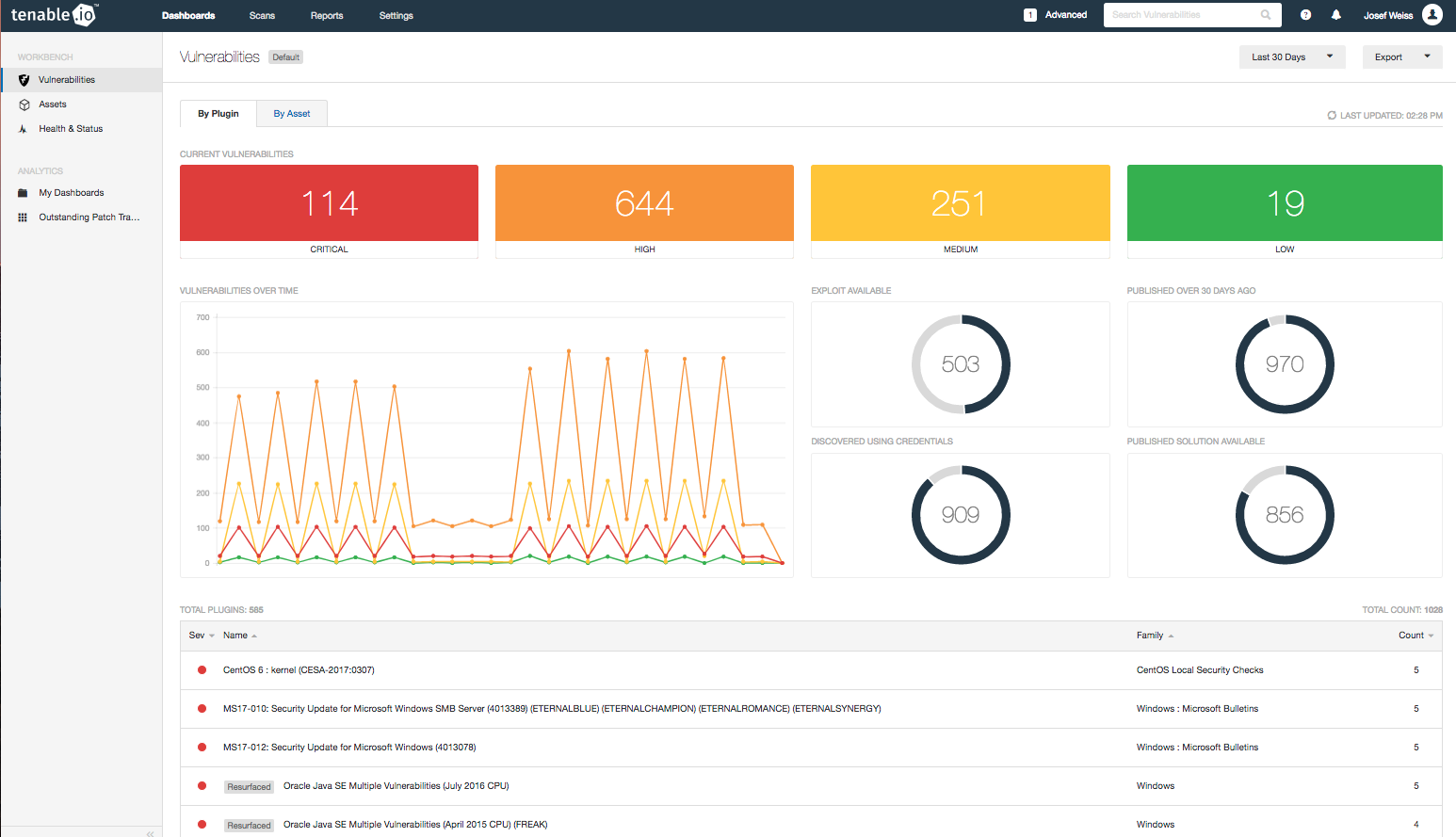
Applying this filter will change the workbench data results (see the next image). You can use this display as a discussion point with administrators and executives. You can also quickly identify the number and severities of the missing patches and available exploits. The trend graph indicates if missing patch counts are increasing or decreasing, and reports how many patches are over 30 days old.
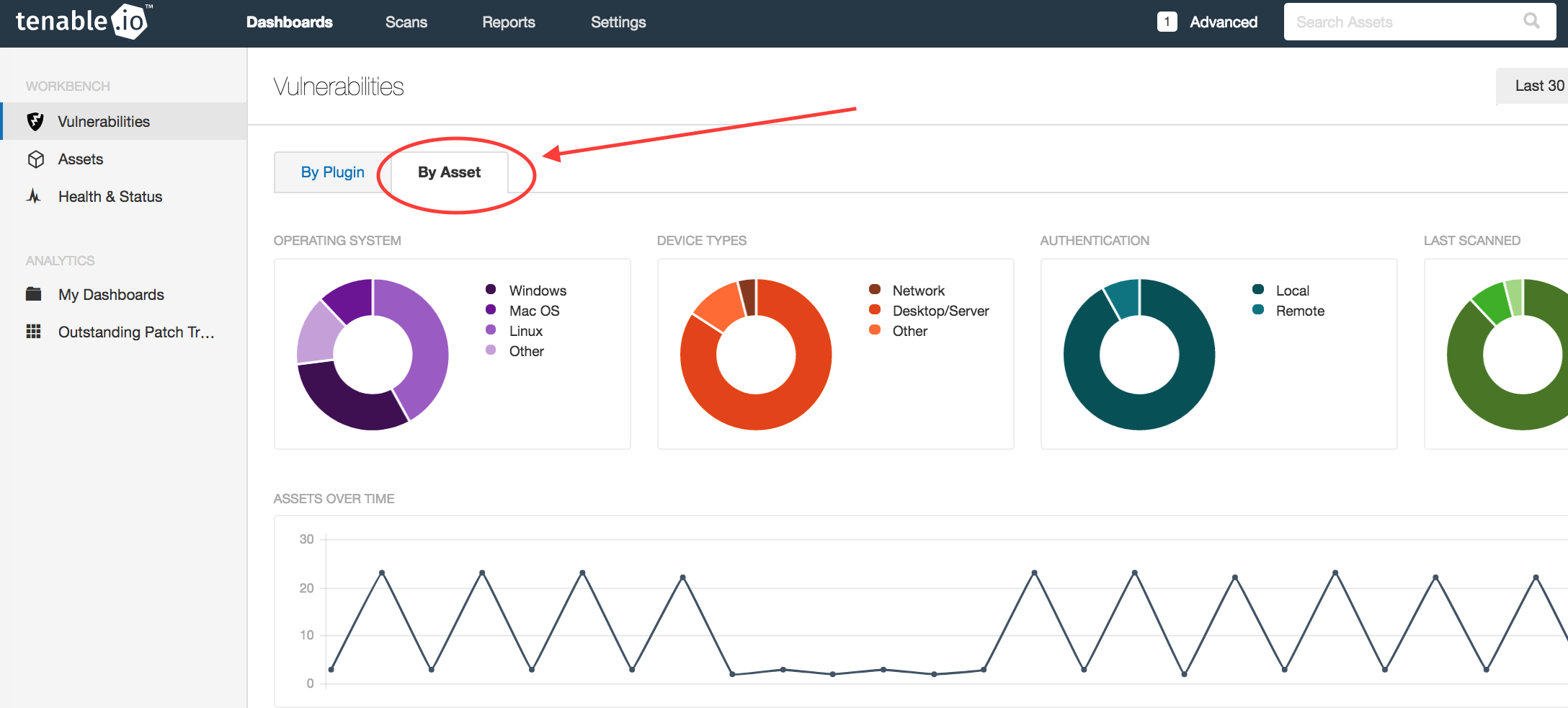
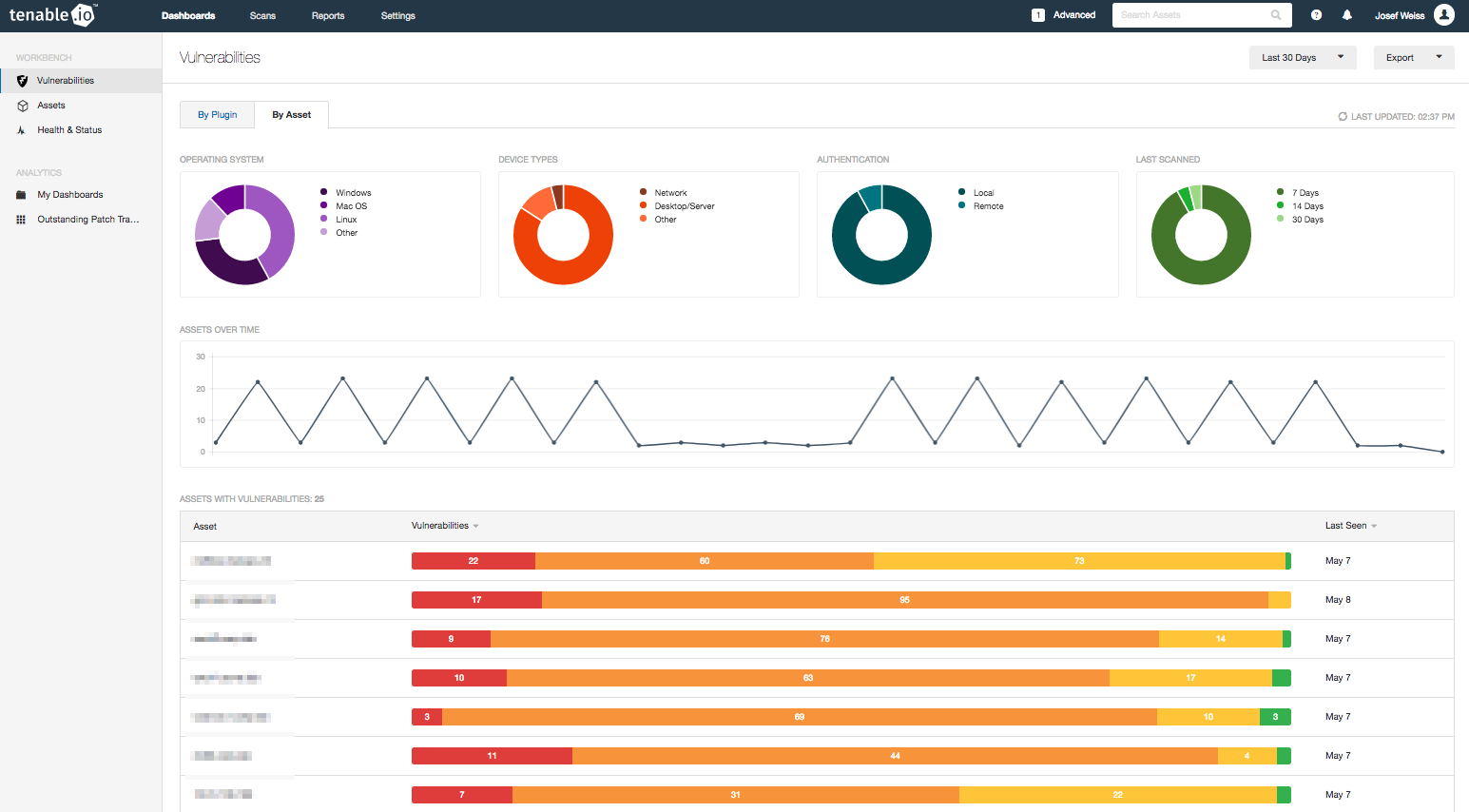
You are not limited to viewing vulnerability data by Plugin on the Workbench. When asked what types of assets are missing patches, click on the By Assets tab.
This Workbench tab displays ring charts that indicate which operating systems and device types are missing patches.
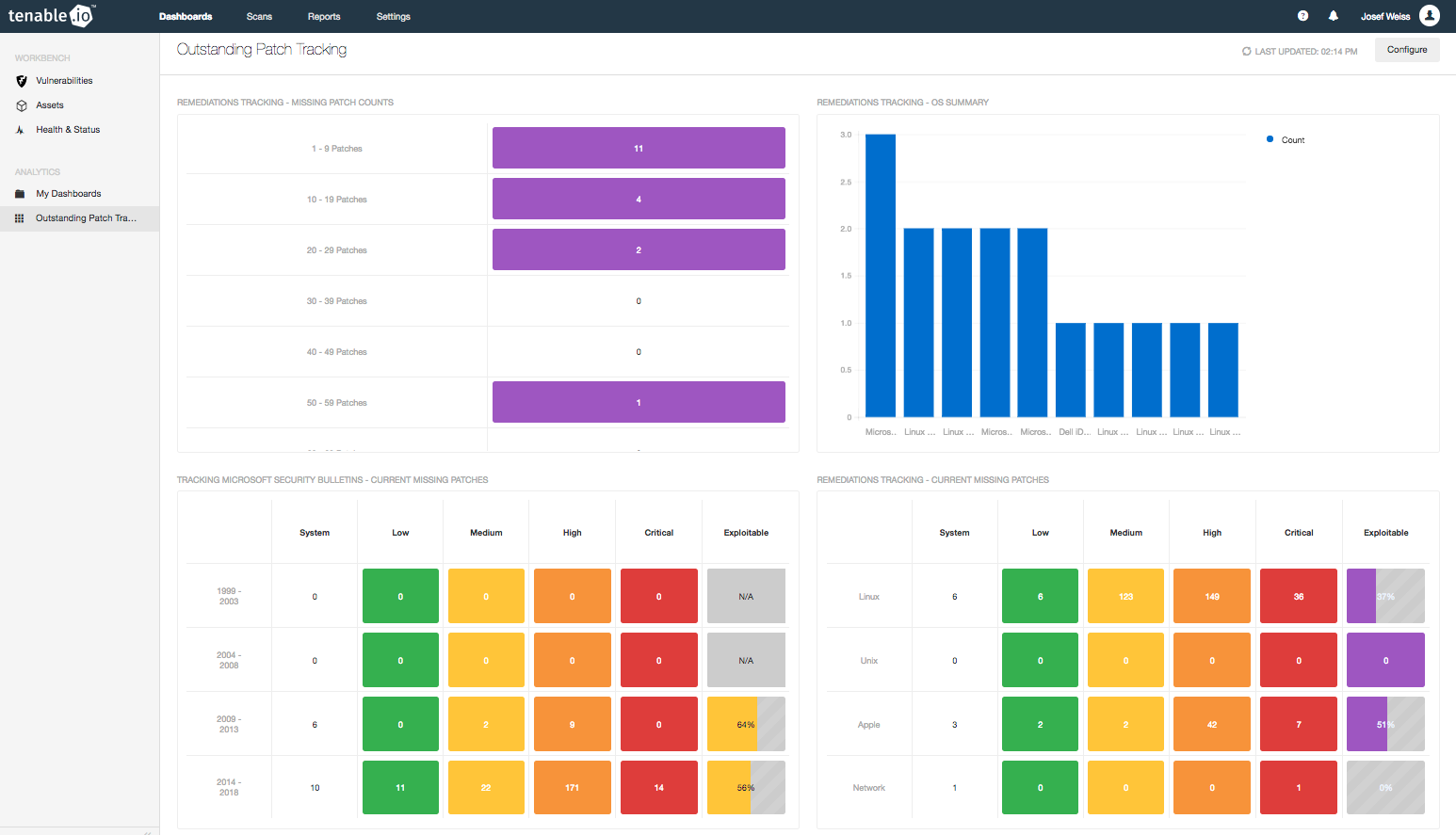
The Outstanding Patch Tracking dashboard and corresponding report provide easy to understand metrics that can be communicated to anyone in your organization.
Tenable.io uses these visual tools to provide insight into the risk exposure of your organization. The vulnerability data enables you to calculate projected costs per vulnerability associated with missing patches, and assists in managing risk. Use this information to effectively discuss the risk potential of delayed patch deployment and its impact on the business with executives.
Use this information to discuss the risk potential of delayed patch deployment and its impact on the business
For more information
Whether you are communicating up the chain, to peers or to your team, Tenable.io provides key analytics to help you address your risk mitigation tasks and to track progress.
Interesting in learning more about Tenable.io?
- Visit the Tenable.io area of our website
- Start a free Tenable.io Vulnerability Management trial
- Executive Management
- Vulnerability Management