Auditing Mobile Device Management (MDM) Platforms with Nessus

BYOD, or Bring Your Own Death as some people jokingly refer to it, has been the bane of IT administrators’ lives ever since the first iPhone was released in 2007. Simply tracking these devices can be a challenge. And many believe mobile devices are a potential security risk. Respondents to a Ponemon State of the Endpoint Report 2015, 75% of administrators believe their mobile endpoints have been the target of malware over the past 12 months. But it doesn't have to be that way. Recent advancements in mobile operating systems and Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms such as MobileIron and AirWatch have tackled and managed this problem. But to extract the most from mobile management, you still need to fine-tune it. With the release of new features in Nessus® 6.4, Tenable has just the right tools to help.
The problem with mobile devices is that, well, they are mobile! They are not affected by traditional security weaknesses such as open ports or insecure services listening in the background, but if you lose a device or someone steals a device, all your personal data—and in some cases even your enterprise data—is at risk. So you need to worry about a different set of problems and plan for different types of contingencies. For example: is remote wipe enabled, does the mobile device have encryption turned on, is the passcode set, and if so, are the complexity requirements met.
There are two ways to verify if these settings are in place. One, either communicate directly with the mobile device itself, or two, simply integrate with the management platform with which the mobile device syncs and check if appropriate policies are in place. With Nessus 6.4, Tenable chose the latter option; it is now possible to audit MDMs such as MobileIron and AirWatch with Nessus.
But hasn’t Tenable already integrated MDMs with Nessus? The answer is yes, but we are now taking that integration to the next level for much deeper control. Read on to see what’s new.
Policy auditing
The advantage of having an MDM is that once you create the right policies, the mobile devices which sync with them automatically fall in line and get configured
The advantage of having an MDM is that once you create the right policies, the mobile devices which sync with them automatically fall in line and get configured. So to secure your mobile assets, it’s imperative to get the MDM policies right, and make sure they are in line with industry standards such as CIS. With the release of Nessus 6.4, Tenable released 10 new policies to do just that for both Apple iOS and Google Android.
What kind of settings do the MDM policies look for?
Protecting mobile devices - The first thing to configure and that most auditors will look for is whether basic security settings are configured: is encryption turned on, is remote wipe enabled, are passcode requirements set, etc. Nessus can now audit all the basic security settings.
Disabling non-essential features - Once you configure basic security settings, the next thing to do is disable all features that are deemed non-essential features for your organization. For example: tethering, Bluetooth, NFC (near field communication), etc. Nessus can audit those as well.
Disabling native apps - You may also want to disable certain native apps, especially those that eat up bandwidth on your network, such as YouTube or FaceTime. In some cases, you may want to go a bit further and disallow the installation of public apps, disallow in-app purchases, or disable explicit content. You can do that with a Nessus MDM audit as well.
Better device inventory
Ever wanted to know which new mobile devices were added, removed or registered since the last scan? Have you had to monitor devices that have not checked in the last X days? You can now do that with Nessus 6.4. You can also find out if a given device is employee owned or not.
Having said that, I would add a disclaimer that not all MDMs are created equal. Some provide rich data for Nessus to audit, and some don’t. Nessus will report on the best level of information available from a given MDM.
MDM action configuration
And finally, another excellent feature supported by some MDMs is the ability to take action if mobile devices are non-compliant. For example, an MDM may block a device from registering if the OS version is less than X. Tenable audit policies will also check whether appropriate actions have been configured on the MDM.
Setting up the scan
Setting up the scan is as simple as creating a new scan and then selecting the MDM Config Audit. A wizard will walk you through setting credentials and audit files. That’s all there is to it.
Scan requirements
Nessus
- Nessus 6.4 or later
- MDM Compliance Audit plugin #81914
- MDM Audit files
AirWatch
- Administration UI login and password
- AirWatch Environment API URL
- AirWatch API Key
MobileIron
- VSP Admin Portal URL
- API Username/Password
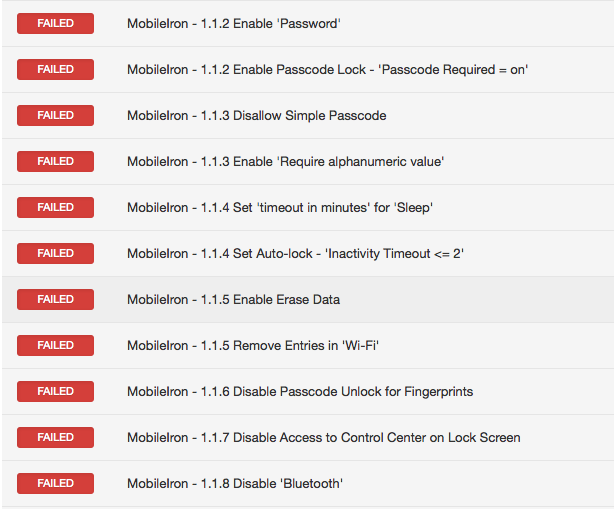
Sample result
A Nessus Pass result will look similar to this:
A Fail result will resemble this screen shot:
Oh, and before you bring out the knives asking for Windows Mobile OS support, let me just say that the MDM Config Audit scan template in Nessus supports that as well. That’s four terrific new audit items.
Conclusion
Make sure that the MDM policies are set up correctly and in accordance with industry standards
If you have mobile devices in your organization, deploying an MDM solution to secure your mobile assets is the first step in the right direction. The next step is to make sure that the MDM policies are set up correctly and in accordance with industry standards. Nessus can now help you do all that to gain control over your BYOD policies. This is just the beginning of MDM integration with Nessus, with more to come.
Updated June 7, 2017.
- Mobile Security
- Plugins
- Vulnerability Management