by Stephanie Dunn
May 10, 2016
Protecting networks against a wide variety of threats can be a complex task for security teams to manage. Monitoring inbound, outbound, and internal network traffic may reveal malicious activity, suspicious connections, and compromised hosts. This dashboard can be used to strengthen network defenses by providing organizations with the critical information needed to detect and remediate threats before critical systems are affected.
Attackers perform reconnaissance to gain access to internal hosts by exploiting vulnerabilities through open ports or services. Compromised internal hosts may be a part of a botnet, and launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against hundreds of external hosts. These attacks may involve malware providing a connection to a command and control (C2) server, and allow confidential data to be exfiltrated. Intrusion detection (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) both monitor network traffic for malicious IP addresses scanning internal hosts, malicious website connections, unauthorized connections to internal hosts, and other suspicious activity. Continuously monitoring network traffic provides the best solution for security teams to adequately protect and defend the network against emerging threats.
Using this dashboard, analysts are able to quickly identify intrusion, scanning, and other threats that have been detected on the network. Many organizations focus on monitoring the perimeter of their network, and do not monitor traffic traversing the network. The Log Correlation Engine (LCE) monitors and collects logs forwarded from IDS and IPS devices, and is constantly updated with lists of malicious IP addresses and websites associated with known botnets. This information can be used to detect malicious port scanning, potential attacks, unauthorized connections, compromised hosts, and other types of suspicious activity. Security teams can use this dashboard to gain a better understanding on how systems are being compromised, and where network defenses need to be strengthened.
This dashboard is available in the SecurityCenter Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the SecurityCenter Feed under the category Threat Detection & Vulnerability Assessments. The dashboard requirements are:
- SecurityCenter 5.3.1
- LCE 4.8.0
SecurityCenter Continuous View (CV) provides continuous network monitoring, vulnerability identification, risk reduction, and compliance monitoring. SecurityCenter CV is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, and new types of regulatory compliance audits. Tenable’s Passive Vulnerability Scanner (PVS) provides deep packet inspection to continuously discover vulnerabilities on the network. Tenable’s Log Correlation Engine (LCE) correlates real-time events, and has the capability to discover users, operating systems, network devices, hypervisors, databases, tablets, phones, web servers, and other critical infrastructure. By integrating with Nessus, PVS, and LCE, SecurityCenter CV’s continuous network monitoring is able to detect events and vulnerabilities across the enterprise.
The following components are included in this dashboard:
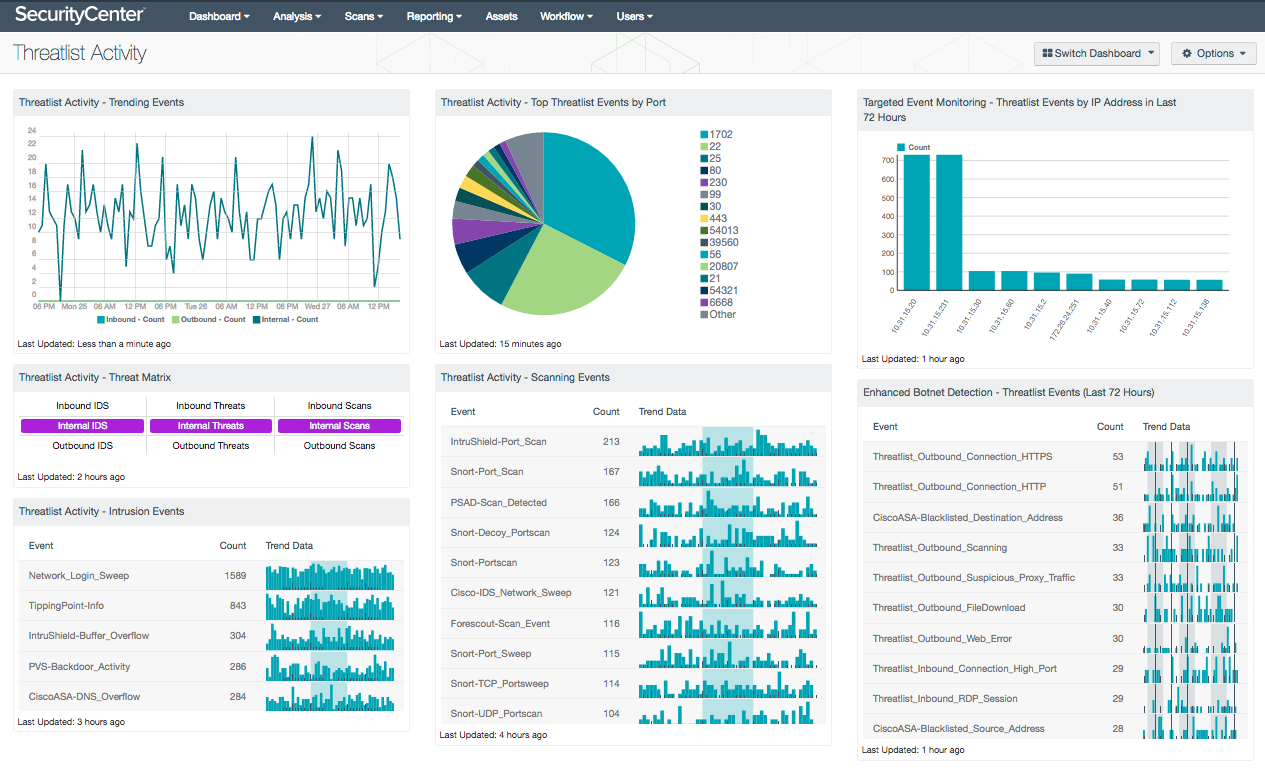
- Threatlist Activity - Trending Events: This component displays a list of inbound, outbound, and internal trending for threatlist activity over the past 72 hours. The LCE maintains a list of hostile IPv4 addresses that are known to be participating in botnets. The LCE considers connection and network events to detect when a hostile IP address connects inbound to your network, as well as when a host on your network connects outbound. Internal hosts connections are also monitored for malicious activity.
- Threatlist Activity - Threat Matrix: This matrix displays IDS, threat, and scanning events from inbound, outbound, and internal network traffic over the last 24 hours. This matrix leverages LCE, which evaluates netflow, sniffed network sessions, connection events from applications, firewall connections, and even file and document downloads reported in real time by the PVS. Analysts can use the information presented within this matrix to quickly identify and remediate compromised hosts.
- Threatlist Activity - Intrusion Events: The Intrusion Events table presents a list of systems reporting intrusion events within the last 72 hours. Events displayed in this table are normalized by LCE to the event type “intrusion”, and include logs from systems reporting potentially malicious attacks, malware, suspicious connections, and more. The analyst can drill down to obtain additional information on the events, and can set the tool to IP Summary that will display the systems on which the events happened. In the analysis screen, setting the tool to Raw Syslog will display the raw syslog of the events, which can give more details.
- Threatlist Activity - Top Threatlist Events by Port: This chart displays the top ports reporting threatlist events within the last 72 hours. Events displayed in this table are normalized by LCE to the event type “threatlist”, and include logs from systems reporting malicious attacks, malware, suspicious connections, and more. This information can alert analysts to ports being used for malicious activity that may have evaded network firewalls. Analysts can drill down to obtain additional information on the events. Event data within this component can be modified to include specific or additional information per organizational requirements.
- Threatlist Activity - Scanning Events: The Scanning Events table displays a list of scanning events that have been detected on the network within the last 72 hours. Events that are normalized by LCE to the event type “scanning” and include logs that indicate systems and applications reporting potentially malicious port scanning activity, network sweeps, network probing, and more. Analysts can drill down to obtain additional information on the events, and can set the tool to IP Summary that will display the systems on which the events happened. In the analysis screen, setting the tool to Raw Syslog will display the raw syslog of the events, which can give more details.
- Targeted Event Monitoring – Threatlist Events by IP Address in Last 72 Hours: The Threatlist Events by IP Address in Last 72 Hours bar chart displays the IP addresses with the highest counts of threatlist events. Normalized events from LCE are filtered for the event type “threatlist,” which is assigned when LCE detects a connection between an internal IP address and a hostile external IP address. LCE maintains a list of hostile IP addresses that are known to be involved in botnets. This component shows the IP addresses that have the most connections to a hostile IP address during the past three days, which could be an indication of malicious activity. The IP addresses identified may need additional hardening, reconfiguration of software, or monitoring of activity.
- Enhanced Botnet Detection - Threatlist Events (Last 72 Hours): The Threatlist Events (Last 72 Hours) table provides a normalized event summary of the threatlist events detected in the past 72 hours by count. The component is filtered by the LCE event type “threatlist” and lists the count and trend of each normalized event. Security analysts can use this table to monitor threatlist events detected in the network.