by Josef Weiss
July 29, 2016
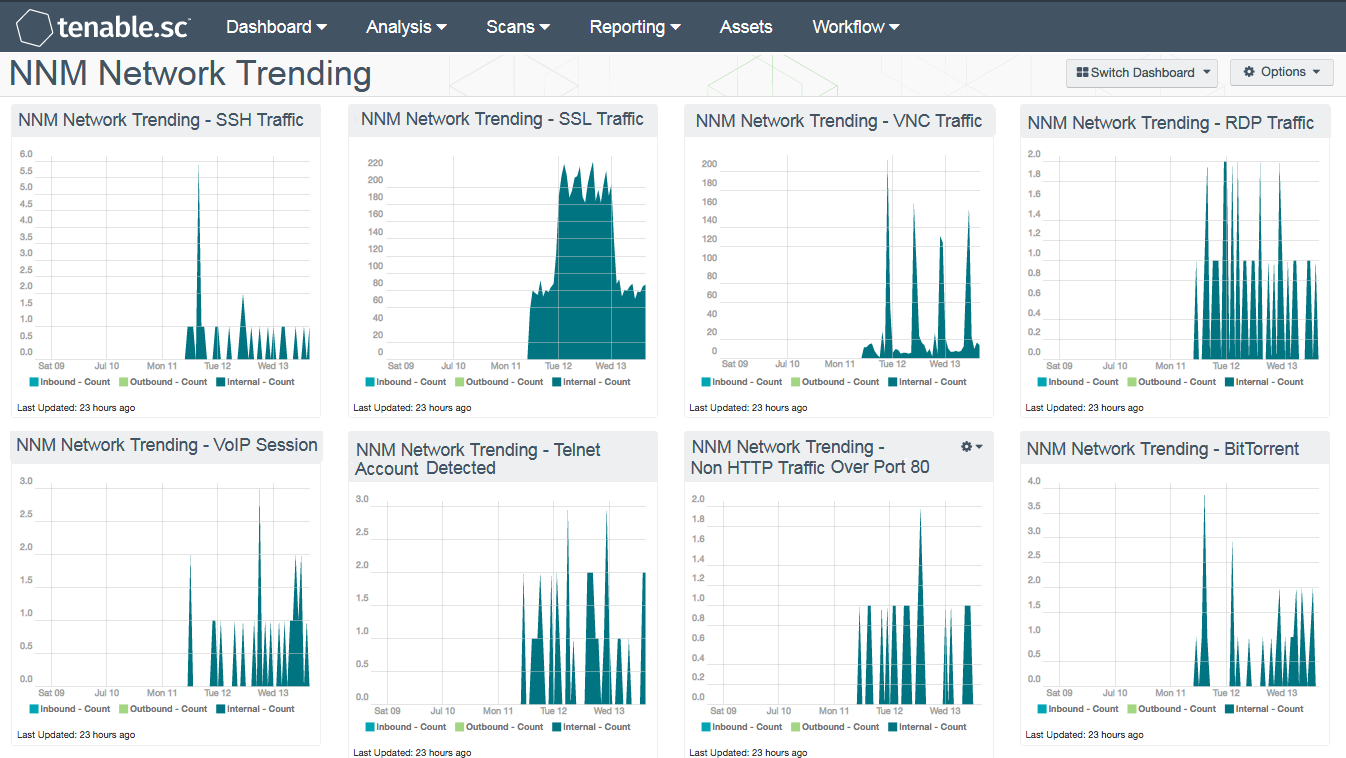
Real-time continuous monitoring of network traffic with Tenable Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) and Tenable Log Correlation Engine (LCE), equips analysts with the required metrics to spot problems and immediately implement solutions. While monitoring network traffic, NNM decodes applications to find vulnerabilities and forwards those to LCE, which normalizes the data. Being able to view real-time metrics in key areas helps organizations identify potential problems, which may have been overlooked otherwise, and take measures to actively prioritize remediation efforts.
Deploying Tenable's Tenable.sc, LCE, and NNM together can generate some amazing features. One of those features is the ability to show normalized network traffic trending. When NNM sends logs to LCE, the LCE normalizes the logs and creates a series of events with the prefix "NNM". This dashboard brings into focus the network event types in 16 easy-to-read trending components.
While monitoring network traffic, NNM continuously collects data on vulnerabilities associated with protocols such as RDP, SSL, Telnet, and SSH. Real-time logs provide a forensic trail of activity, and ideally logs should be collected from all systems. If this is not possible, NNM can assist by providing analysts with a view into administration activities and potential abuse passively.
In large enterprise organizations, logging may only be enabled on mission critical systems, and not others. For example, the Windows event logs may be collected centrally, but the use of VNC or cloud-based services may not be logged. NNM provides additional coverage in detecting network sessions, which can be useful in detecting anomalous events or malicious traffic.
NNM has the ability to detect network protocols that are using non-standard ports, for example, traffic using port 80 that is non HTTP protocol and non FTP traffic over port 21. Attackers can exploit non-standard ports to compromise a system and attack other systems on the network. Collecting the logs for such traffic can be critical during a network compromise, and aids in the ability to forensically track the monitored traffic.
Each of the components display the normalized event in the following three traffic flows:
- Inbound – Traffic from IP addresses considered external to your network, going to addresses that are internal to your network.
- Outbound – Traffic from IP addresses considered internal to your network, going to addresses that are external to your network.
- Internal - Traffic between IP addresses that are considered internal.
This dashboard is available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Monitoring.
The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 4.8.2
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
Tenable's Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) provides continuous network monitoring, vulnerability identification, risk reduction, and compliance monitoring. Tenable.sc CV is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, and new types of regulatory compliance configuration audits. Passive listening continuously collects data and monitors network traffic and services for malicious activity and anomalous behavior. Host data uses logs to actively monitor system activity and events from applications, cloud infrastructure, trust relationships, and network services. Using Tenable.sc CV, an organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of its network activity across the enterprise.
The dashboard contains the following components:
- NNM Network Trending – SSH Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the SSH traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – SSL Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the SSL traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – VNC Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the VNC traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – RDP Traffic: LCE provides a trending view of the RDP traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – VoIP Session: LCE provides a trending view of the VoIP traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network.
- NNM Network Trending – Telnet Account Detected: The LCE provides a trending view Telnet traffic by discovering clear text credentials traversing the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – Non HTTP Port 80 Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the Non HTTP Port 80 traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – BitTorrent Traffic: LCE provides a trending view of the BitTorrent traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – FTP Client Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the FTP Client traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – FTP Non-Standard Port Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the FTP Non-Standard Port traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – FTP Server Traffic: LCE provides a trending view of the FTP Server traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending – POP Traffic: The LCE provides a trending view of the POP traffic discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.
- NNM Network Trending - Cloud Data: LCE provides a trending view of the SSL traffic from clients to services that have been associated with a cloud file storage service. Analysts should monitor this activity closely, as these events may indicate users transferring confidential data to externally hosted cloud service providers.
- NNM Network Trending – IP Protocol Tracking: LCE provides a trending view of the IP Protocol Tracking discovered by the NNM nodes on the network.
- NNM Network Trending – MAC Addition: LCE provides a trending view of MAC address detection discovered by the NNM nodes on the network.
- NNM Network Trending – DNS Tunnel Activity: The LCE provides a trending view of the DNS Tunnel activity discovered by the NNM nodes on the network. Spikes presented within the component may indicate botnet communication, attacks, and other forms of malicious activity.