by Cesar Navas
July 9, 2020
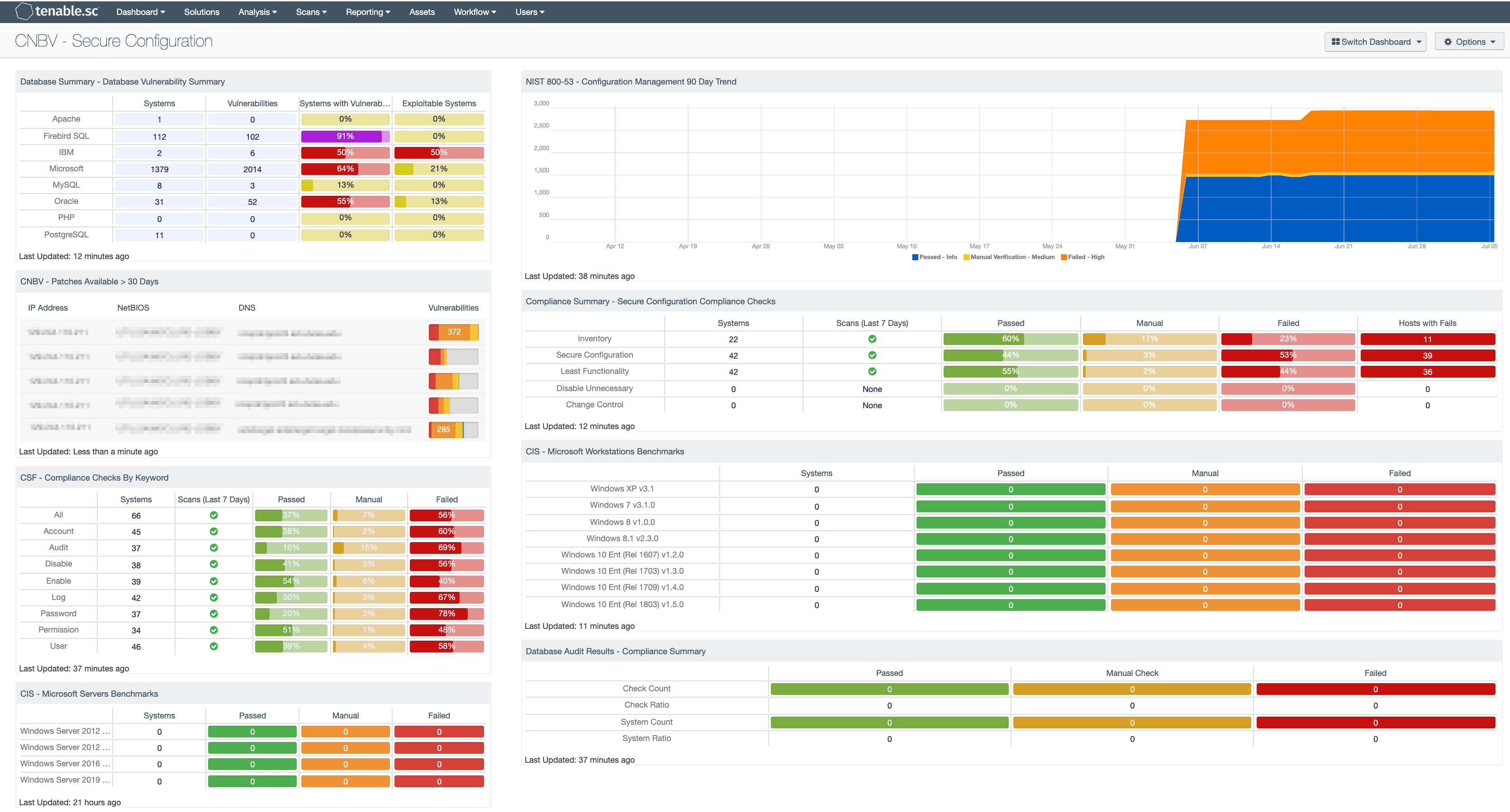
The National Banking and Securities Commission (CNBV) Annex 72 is a collection of Key Risk Indicators (KRI) that establish compliance standards for financial institutions operating in Mexico. Financial institutions in Mexico should be prepared to divulge cyber risk KRIs to CNBV when requested. The KRIs relating to secure configuration management are grouped by asset function, for example the servers, workstation, network devices, and other asset types. Within each of these asset categories, there are KRI’s that require hardening standards for the OS, applications, and other security related tasks. This dashboard relates to the following KRIs: KRI0003, KRI0004, KRI0025, KRI0028, KRI0029, and KRI0030.
CNBV’s Annex 72 requires institutions to know the percentages of systems which have been missing available patches for more than 30 days. Tenable.sc assists in tracking when patches are applied by tracking the date of install through mitigation tracking. This tracking process helps the CISO to accurately report on when the latest security patches have been applied across the network. Risk managers can find more details about the mitigation requirement in KRI0028-30.
Tenable.sc provides a series of audit checks against the CIS benchmarks. These benchmarks provide institutions with a set of generally accepted best practice guidelines to better harden their information systems. By implementing these hardening guidelines, institutions can meet and exceed many compliance standards. KRI0003 and KRI0004 provide guidance for system level hardening guidelines. Tenable.sc uses the CIS audit files with a cross-reference to map many different controls for example ISO 27000, PCI-DSS or the Cybersecurity Framework.
This dashboard provides organizations the risk manager the ability to report and analyze KRI described in CNBV Annex 72.
This Dashboard is available in the Tenable.sc feed, which is a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The Dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc feed under the Executive category. The dashboard requirements are as follows:
- Tenable.sc 5.14.1
- Nessus 8.10.1
- Compliance Data
This dashboard provides the organization with a clear and simplified method to identify and establish compliance according to Annex 72 by CNBV. The data can be Analyzed to provide more detail in non-compliant areas, which facilitates the Fix and Measuring steps to the Cyber Exposure Lifecycle. Tenable.sc is the On-prem solution for understanding the picture of the network, while keeping the data under the organization’s control. Built on leading Nessus technology, Tenable.sc discovers unknown assets and vulnerabilities, and monitors unexpected network changes before they turn into breaches.
Components
Database Summary - Database Vulnerability Summary: The Database Vulnerability Summary component displays various defined database applications by row, and enumerates any found vulnerabilities across the columns. Presented are the number of systems on which the technology has been located, the number of identified vulnerabilities, the ratio of vulnerable systems, and the ratio of how many are exploitable.
NIST 800-53 - Configuration Management 90 Day Trend: This component displays an area trend chart of compliance checks related to an organization's configuration management. Green = Passed, Orange = Manual Verification Required, Red = Failed.
CNBV - Patches Available > 30 Days: This table displays the hosts which have patches that have been available for more than 30 days. By viewing vulnerabilities based on their patch release date, you are able to easily identify the systems with risks that are well passed recommended patch cycles. Most organizations require patches to be installed within 30 days of the patch release. Regardless if this risk was only first identified or not, these are systems with long outstanding risks and should be mitigated as soon as possible. Both actively and passively discovered vulnerabilities are included.
Compliance Summary - Secure Configuration Compliance Checks: This component presents the results of compliance audits to verify the secure configuration of systems, including least functionality, disabling unnecessary services, and inventory and change control settings. Each row includes the system count, whether scans were performed in the last seven days, and the percentage of checks that passed, failed, or require manual verification. Passed checks are displayed in green, failed checks are in red, and checks that require manual verification are in orange. The count of hosts with failed checks is also given. Clicking on a highlighted indicator will bring up the vulnerability analysis screen to display details on the compliance checks and allow further investigation. In the vulnerability analysis screen, setting the tool to Vulnerability Detail List will display the full details on each compliance check, possibly including further information such as the expected and actual policy values and the specific sections of the various standards to which the compliance check relates.
CSF - Compliance Checks By Keyword: This component uses results from the compliance audit to trigger on specific plugin keywords. Each column includes the respective keyword along with the host count, scans performed in the last 7 days, and whether the checks have passed, failed, or require manual verification. Passed checks are green, failed are red, and checks that require manual verification are in orange. This component will allow the analyst to readily identify specific compliance vulnerabilities. The keywords can be modified to suit organizational needs.
CIS - Microsoft Workstations Benchmarks: This matrix component presents a summary of audit checks performed on systems running Microsoft Workstations. The “Systems” column includes a count of the number of systems scanned against the audit check, and shows whether the operating system, service, or application is installed. Lack of results within the “Systems” column may highlight systems where the object in question is not installed, or the scan needs to be modified. The “Passed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check passed the defined threshold within the CIS benchmark. The “Manual Check” column displays the number of scan results which require a manual review of the audit check to determine a pass or fail. The “Failed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check was outside of the defined parameter in the CIS benchmark. These failed results should be addressed immediately.
CIS - Microsoft Servers Benchmarks: This matrix component presents a summary of audit checks performed on systems running Microsoft Servers. The “Systems” column includes a count of the number of systems scanned against the audit check, and shows whether the operating system, service, or application is installed. Lack of results within the “Systems” column may highlight systems where the object in question is not installed, or the scan needs to be modified. The “Passed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check passed the defined threshold within the CIS benchmark. The “Manual Check” column displays the number of scan results which require a manual review of the audit check to determine a pass or fail. The “Failed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check was outside of the defined parameter in the CIS benchmark. These failed results should be addressed immediately.
Database Audit Results - Compliance Summary: When performing configuration audit of systems in accordance with a GRC program, security analysts can benefit from a summary view of the data set. The Database Compliance Summary table provides a high-level view of the Database compliance status. The first two rows provide the total count of Passed checks, Failed checks, and checks requiring a manual review. The first row, 'Check Count', provides a count of the current checks per check status. The second row, 'Check Ratio', provides a ratio view of check status. The three columns together should total 100%.